In the digital age, where privacy is paramount, the use of incognito mode, synonymous with private browsing or privacy mode, has become a common practice. It provides a shield against the local storage of your browsing history, cookies, and cache, offering a semblance of online anonymity. However, the veil of incognito browsing raises questions—what happens to your incognito history? While the browser itself doesn’t save your activity, remnants may persist, prompting the need to uncover your past incognito journeys. As we delve into the intricacies of “How To View Incognito History,” this article serves as your guide, offering insights on retrieving incognito history, dispelling myths, and providing step-by-step instructions on checking and deleting your private browsing records. Whether you’re a privacy-conscious individual or simply curious about the inner workings of incognito mode, join us in exploring the nuanced world of online privacy and secure browsing.
About Incognito Mode
Incognito mode, a standard feature in contemporary web browsers, serves as a privacy-enhancing tool by allowing users to browse the internet without leaving a trace in the browsing history. Contrary to standard browsing, incognito mode ensures that your browsing history is not stored locally, which is particularly useful when sharing a device and aiming to keep your online activities private. In addition to omitting browsing history, incognito mode disables autofill, preventing the browser from remembering usernames, passwords, and other form data. This feature proves beneficial when using public computers or someone else’s device, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to login credentials.
Moreover, incognito mode imposes limitations on cookies and tracking mechanisms, making it more challenging for websites to monitor and serve targeted advertisements based on your online activities. While it enhances privacy to a certain extent, it’s crucial to note that incognito mode does not grant complete anonymity. Despite preventing local storage of browsing history, your internet service provider (ISP), network administrators, and visited websites can still track your online activities. Importantly, incognito mode does not offer additional security measures, making users susceptible to malware, phishing attacks, and other online threats. Furthermore, it does not conceal your activities from the websites you visit, as website owners, ISPs, and network administrators can monitor your online behavior. Understanding these aspects of incognito mode is vital for informed and secure browsing practices.
Does incognito mode save browsing history?
No, incognito mode does not save your browsing history. When this mode is activated, the browser ensures that no record is kept of the websites visited, search queries entered, or the cookies and temporary files associated with the browsing session. The intention is to provide users with a browsing experience that leaves no local trace, which is particularly useful when privacy is a priority.
However, it’s important to note that while the browser itself doesn’t store the history, there are certain methods that could potentially reveal what someone browsed in incognito mode. This detection doesn’t occur within the browser but rather involves checking the DNS cache on the computer or using third-party apps or browser extensions. It’s worth emphasizing that the use of such obscure apps or extensions may introduce privacy and security risks, so careful consideration is advised before employing any third-party tools for this purpose. Understanding the limitations and potential risks associated with incognito mode can contribute to a more informed and secure browsing experience.
How to View Incognito History?
Unlocking the mysteries of your incognito history can be essential, whether for curiosity’s sake or to maintain control over your digital footprint. While incognito mode is designed to keep your browsing history discreet, there are methods to view it, depending on your device and operating system. In the following sections, we’ll guide you through the steps for various platforms, including Windows PC, MacOS, and both Android and iOS devices. Let’s explore the techniques to unveil your incognito history and gain insights into your past online activities.
On Windows PC
If you’re using a Windows device and curious about uncovering your incognito history, it’s worth noting that the Domain Name System (DNS) cache plays a crucial role. The DNS matches website URLs with their respective IP addresses, and this information is stored in the DNS cache to expedite your browsing experience. Even when you’re in incognito mode, your DNS cache retains data related to the websites you’ve visited.
To check your incognito history via the DNS cache on a Windows device, follow these steps:
- Open the Start menu on your Windows device.
- Type “cmd” in the search bar to open the Command Prompt.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator” to ensure you have the necessary permissions.

- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command:
- Press the Enter key to execute the command.
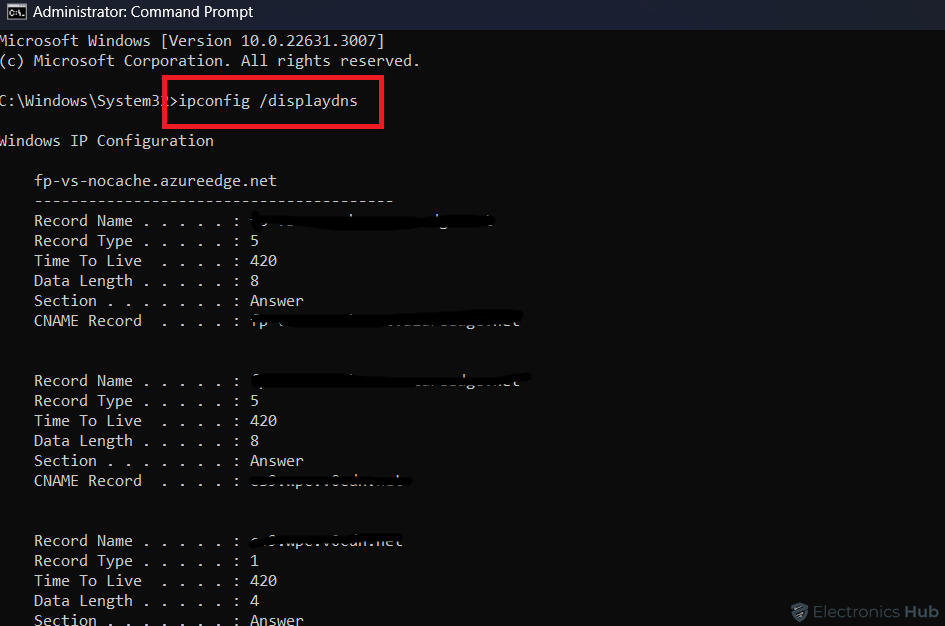
After executing these steps, you’ll see a display of your DNS cache history. This includes information about the websites you’ve visited, even in incognito mode. If you need to recover or clear your incognito history, this method provides insights into your past online activities stored in the DNS cache on your Windows PC.
On MacOS
When it comes to discovering incognito history on MacOS, the DNS cache holds the key. Similar to Windows, the Domain Name System (DNS) cache on MacOS records the translation of website names into IP addresses to streamline future visits. This cache, which retains records of the sites you visit, can be accessed, although the process involves using both the Console and Terminal applications.
To check your incognito history via the DNS cache on MacOS, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Applications > Utilities and open the Console application.
- In the sidebar under Devices, select your Mac.
- In the search box, type the following:
- Press the Start button in the toolbar to initiate the search.
- Go back to Applications > Utilities and open the Terminal application.
- Type the following commands into Terminal:
| sudo killall -INFO mDNSResponder |
- Press the Enter key to execute the command.
- Type in your admin password when prompted.
- Go back to the Console app, and you’ll be able to view the cached DNS records, including information about the sites visited in incognito mode.
On Android and iOS Devices
While it’s important to note that directly retrieving incognito history using DNS cache on mobile devices may not be possible, it’s essential to be aware of potential privacy risks. On smartphones, particularly Android and iOS devices, users can set up their phones to record incognito browsing history using third-party tracking apps. Parental control apps, designed for monitoring children’s online activities, can reveal detailed browsing logs, even in incognito mode.
However, it’s crucial to exercise caution, as this service, while helpful for parents monitoring their children’s online behavior, poses potential threats to personal privacy. These browser history reports provide comprehensive details about the websites visited or searched, including incognito mode activity, along with timestamps and frequency of visits. Some apps go even further by collecting keystroke records during private browsing sessions.
For those interested in exploring such monitoring apps, here are some popular parental control apps to view incognito search history:
- Famisafe
- KidsGuard Pro by ClevGuard
- Spyzie
- Hoverwatch
- Qustodio
- mSpy
It’s important to use these apps responsibly and consider the implications of monitoring private browsing activities. Additionally, always adhere to legal and ethical guidelines when using tracking or monitoring tools on mobile devices.
How To View Incognito Browsing History Using Chrome Extensions?
While it’s generally discouraged to use Chrome extensions that claim to record incognito history due to privacy concerns, one exception to explore cautiously is “Off The Record History.” This extension provides more flexibility with incognito browsing by allowing users to save their history for a limited time and delete it manually. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use this extension to find incognito history in Google Chrome:
- Open Off The Record History and click “Add to Chrome.“
- Confirm the installation by clicking “Add extension” in the pop-up that appears.
- Go to Extensions by Entering “chrome://extensions/” in the URL bar and click “Details” under the Off The Record History extension.
- Scroll down to find the “Allow in Incognito” option and toggle it on. This setting enables the recording of history even in incognito mode.
- With the extension activated, it will automatically record incognito history. Note that the extension deletes incognito history after seven days.
- Users can also manually delete incognito history in Chrome by going to the settings for the Off The Record History extension.
Mac users looking to take advantage of this extension may want to download Chrome for Mac, and Windows users can explore changing their default browser.
How to Delete Incognito History?
Under normal circumstances, you don’t need to take any specific actions to delete incognito history, as it is not saved by your browser. However, for those who are particularly concerned about their online privacy and want to eliminate any potential traces of incognito browsing, there is an option to clear the DNS cache on various devices. This additional step can be taken to ensure that any records stored in the DNS cache are also removed. Now, let’s explore how to perform this action on different devices to enhance your privacy and security.
On Windows PC
When it comes to ensuring the deletion of incognito history on a Windows PC, clearing the DNS cache is a straightforward process. This action helps eliminate any potential traces stored in the cache. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Click on the Start menu located in the bottom left corner of your screen.
- In the search bar, type “cmd” to open the Command Prompt.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator” to ensure you have the necessary permissions.
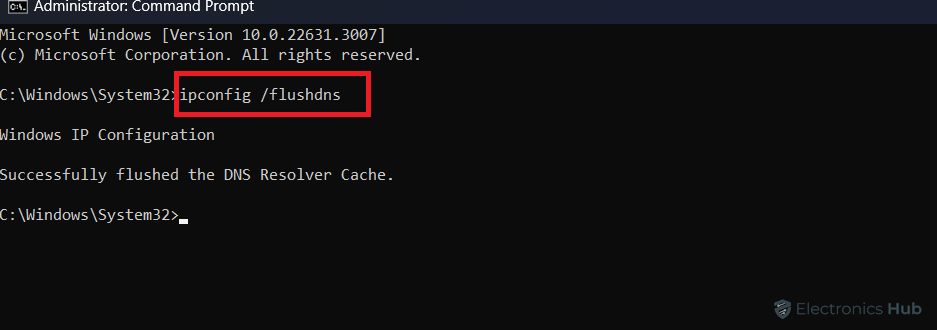
- In the Command Prompt window, enter the following command:
- Press the Enter key to execute the command.
On MacOS
Deleting incognito history on MacOS involves clearing the mDNSResponder, which is responsible for translating website names into IP addresses. Here’s a concise guide to perform this action:
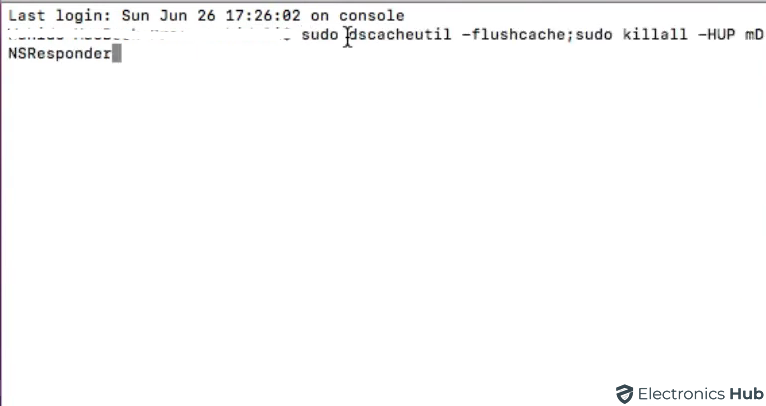
- Navigate to Applications > Utilities and open the Terminal application.
- In the Terminal window, type the following command:
| sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder |
- Press the Enter key to execute the command.
- You will be prompted to enter your admin password. Type it in and press Enter.
On Android and iOS Devices
Deleting incognito history on mobile devices, both Android and iOS, involves clearing the DNS data. Follow these steps to ensure the removal of any potential traces:
On Android:
- Launch the Google Chrome browser on your Android phone.
- In the address bar, type the following:
| chrome://net-internals/#dns |
- From the left panel, select “DNS,” then tap “Clear host cache” to clear the DNS data and delete your incognito history.

On iOS Devices (iPhone & iPad):
- Swipe up from the bottom of the screen to open your iPhone’s Control Center.
- Tap the airplane icon to enable Airplane Mode. This action temporarily disables Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and your phone’s signal, automatically clearing your DNS cache.
- Tap the Airplane Mode icon again to turn it off and use your phone normally. Repeat these steps every time you want to delete your incognito history on your iPhone.
How to Hide Browsing History in Incognito Mode?
While incognito mode provides a convenient way to ensure that your browsing history is not easily visible to others who use your computer, it’s essential to recognize that certain third parties may still have access to your online activities. These parties include:
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): ISPs have the capability to monitor and track your online activities, even when using incognito mode.
- Websites and Online Services: Visiting websites or using online services may lead to the collection of information about your online activities by the respective platforms.
- Government Agencies: Depending on your jurisdiction, government agencies may have the authority to monitor online activities for security, law enforcement, or intelligence purposes.
- Network Administrators: If you are using a network provided by an organization, such as a school or workplace, network administrators can monitor and log your internet activities.
To enhance the privacy of your browsing, whether in incognito mode or otherwise, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, rendering it indecipherable to anyone not directly involved in the communication. Additionally, it assigns you a different IP address, making it significantly more challenging for anyone to identify you or build a profile based on your online interests. Utilizing a VPN is a straightforward and effective way to hide your browsing history from various third parties and safeguard your online privacy.
View and Delete Incognito History? – FAQs
Ans: No, incognito mode is designed not to save your browsing history locally on your device. However, it’s important to note that traces may still exist in other areas, and certain methods, such as checking the DNS cache, can potentially reveal incognito history.
Ans: To clear incognito history on Windows, users can flush the DNS cache by opening the Command Prompt as an administrator and entering the command ‘ipconfig /flushdns.’
Ans: Yes, on Android devices, users can clear incognito history by accessing Chrome’s net-internals settings. On iOS devices, enabling and disabling Airplane Mode clears the DNS cache, removing potential incognito history traces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while incognito mode provides a layer of privacy by not saving your browsing history locally, it isn’t foolproof. Your ISP, network administrators, and visited websites can still track your activity. For true anonymity, consider alternative browsing methods like Tor or VPNs. Remember, responsible practices like clearing your DNS cache and exercising caution with browser extensions can further enhance your online privacy. By understanding the nuances of incognito mode and taking informed steps, you can navigate the digital world with greater control and confidence over your online footprint
Credit : Source Post






